Explain the Different Stages of Soil Formation
Geological cycle has four cyclic steps. Soils that develop in grasslands will be remarkably different than soils that develop in forests.

How Is Soil Formed From Parent Material Quora
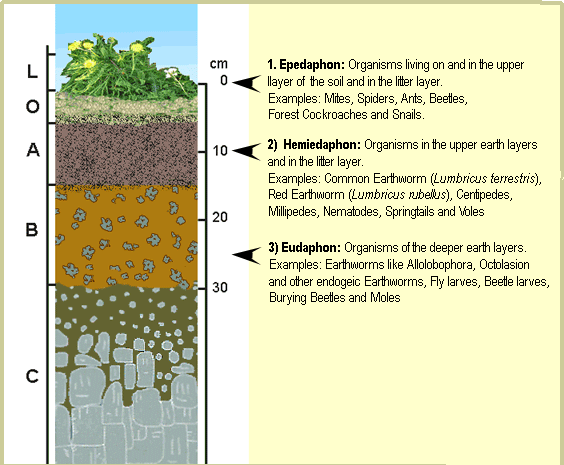
B the layer of accumulation of clay iron and other elements from the overlying soil.
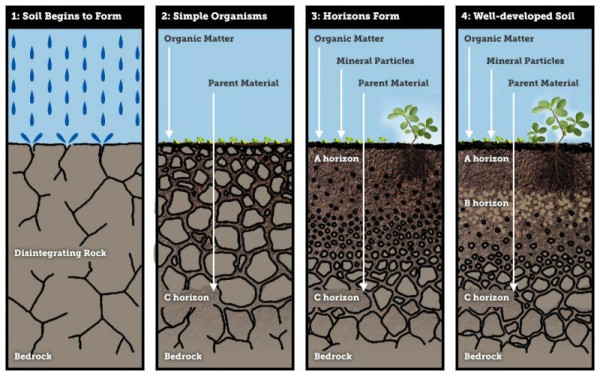
. Mohr and Van Barren have recognized five stages in the development of soils in relation to time. 6 Steps in soil formation STUDY Flashcards Learn Write Spell Test PLAY Match Gravity Created by Avery_Waller Terms in this set 6 The rock weathers Step one The plants begin to grow Step two Animals such as insects and worms start to appear Step three The plants and animals die and decay Step four Humus forms Step five. Soil formation is a process of two distinct phases.
Different types of roots have different effects on soils. 2 Losses of mineral and organic matter from soil. Ie the topography of the.
Everything takes a very long time indeed. Easily weatherable minerals have been decomposed for the greater part. Rocks are broken into three major groups.
Sedimentary igneous and metamorphic. Iii Translocation of mineral and organic matter from one point of soil profile and deposited at another horizon. Other times it forms through chemical weathering where weak acids.
The formation of true soil from Regolith The evolution of true soil from regolith takes place by the combined action of. Ii The development or the formation of true soil by some soil forming factors and pedogenic process hope it will help you. Soil formation or pedogenesis is the process of evolution of soil under the influence of various physical biological climatic and geological factors.
Animals and micro-organisms mix soils and form burrows and pores. Time is perhaps the most important factor when it comes to soil formation. Denudation is the abrasion of present rock material by the action of ice water or wind.
The Performing Stage mainly characterized by overall synergy. C the layer of incomplete weathering. Soil formation factors and processes The soil formation is the process of two consecutive stages.
Stages of Soil Formation. An animated version of the rock cycle can be found at the British Geological Society website. Soil formation is a process strongly driven by the boundary conditions.
As soils form nutrients are being continually removed from and added to the soil with time. The Norming Stage mainly characterized by cooperation integration and unity. A fourth factor of soil formation is the configuration of the landscape.
Like humans soils have different properties based on where they are from and where they grew up formed. The soil formation process depends upon the presence of new soil material which is either acquired by denudation or deposition. The fundamental process of soil formation are the following.
Rainwater sips in rocks and the fluctuation in temperature causes differential expansion and contraction of the rocks. The document has moved here. He left the in case there were other factors that he had not considered at the time.
Types of Soils Triangle. Soil Formation Processes details how new soil can appear in a new location and how soil looks change over time. This soil formation factor is intimately influenced by climate.
S soil formation. The fundamental process of soil formation are as follows. Pedogenesis is a cyclic phenomenon called geological cycle.
Deposition is the accumulation of new materials that have been eroded from another place such as river gravels or blown gravel or the creation of new rocks. The process of soil formation is called Pedogenesis. I Weathering of rocks and minerals ie.
Soil and soil formation can. Some soil forms from rock through a process known as mechanical weathering. Plant roots open channels in the soils.
Topography which modifies the water relationship in soils and to a considerable extent influences soil erosion is usually treated as a soil former. Then the freezing and thawing of the water captured inside the rocks creates cracks inside the rocks. These layers can then be separated on the.
Ii Losses of mineral and organic matter from soil. Soil fertility is greatly influenced by the factors of soil formation. The Forming Stage mainly characterized by team orientation.
Weathering just started but much of the original material is still un-weathered. Weathering is the breakdown of rocks and minerals into soils. Grass roots are fibrous near the soil surface and easily decompose adding organic matter.
R relief or topography p parent material. The rock cycle illustrates how these different types of rocks form. These horizons are often present in.
Soil Formation Surface And Groundwater Weathering and Soils. Disintegration physical and decomposition chemical of rocks and minerals. The Storming Stage mainly characterized by a power struggle.
I Addition of mineral and organic matter to the soil. Plants animals micro-organisms and humans affect soil formation. 3 Translocation of mineral and organic matter from one point of soil profile and deposited at another horizon.
E the eluviated leached layer from which some of the clay and iron have been removed to create a pale layer that may be sandier than the other layers. Soils have 6 major horizontal layers or horizons that can be present. 1 Addition of mineral and organic matter to the soil.
Soil formation occurs via a series of changes to the parent material all of which lead to the formation of layers of soil also called soil horizons. The weathering of rock R into Regolith 2. Meaning of Soil Formation.

How Do Soils Form New Zealand Soils Portal Manaaki Whenua Landcare Research

How Soils Form Environment Land And Water Queensland Government
Comments
Post a Comment